Hungarian GP 2025: Strategy, Pit-Stop Tech, and Tire Dynamics
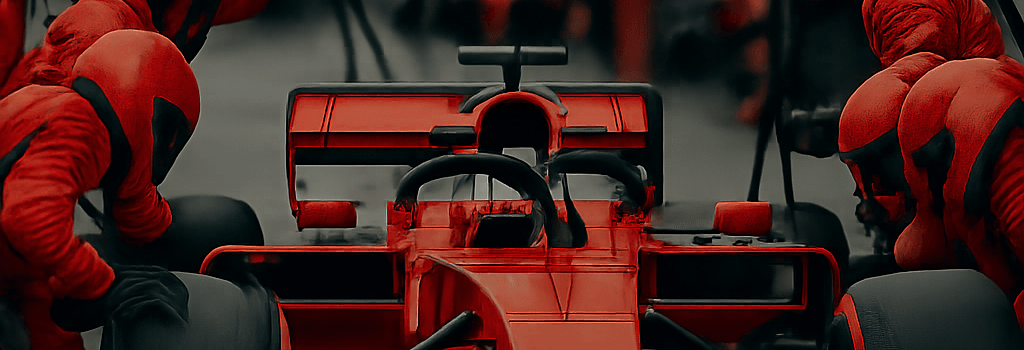
The 2025 Hungarian Grand Prix at the Hungaroring once again proved that in Formula 1, victory is won or lost in the garage as much as on track. From refined pit-stop machinery to cutting-edge tire compounds and aerodynamic tweaks, this race weekend showcased the sport’s latest technical advancements. As teams enter the monthlong summer shutdown, let’s dissect how strategy, engineering, and real-time data analysis shaped the outcome.
Race Overview and Historical Context
Since its inauguration in 1986 behind the former Iron Curtain, the 4.3 km Hungaroring’s twisty layout has earned the moniker “Monaco without the walls.” Overtaking remains notoriously difficult, placing a premium on qualifying performance and pit-stop execution. Last weekend’s results echoed this trend, with less than 0.9 s separating 19 cars in Q1 and Q2—data from the FIA shows a departure from larger gaps seen at high-speed circuits.
Qualifying Shocks
- Pole Position: Charles Leclerc stunned the paddock by outpacing both McLarens in Q3, aided by a sudden 5°C drop in track temperature that favored Ferrari’s revised suspension geometry.
- McLaren Challenge: Lando Norris and Oscar Piastri locked out P2–P3, though gusting crosswinds exposed weaknesses in their underfloor vortex stability.
- Red Bull Decline: Max Verstappen struggled with rear-wing balance, qualifying only P8—a rare misstep traced to a lineage of porpoising-related setup compromises.
Strategy Duel: Undercut vs. Overcut
On a circuit where slipstream opportunities are minimal, pit strategy becomes the main overtaking tool. Ferrari elected an early two-stop approach for Leclerc, banking on fresher soft-compound Pirelli C5 tires to undercut McLaren. McLaren countered with a one-stop overcut strategy for Norris, extending his stint on Medium-compound C3 rubber to preserve track position.
- Leclerc’s first stop at Lap 20: 2.0 s stationary — engineers optimized wheel-gun torque profiles to reduce wheel nut change time by 12%.
- Piastri mirrored Leclerc at Lap 21, leveraging predictive pit-lane traffic algorithms to slice a critical 0.1 s off transit time.
- Norris delayed until Lap 35, executing a 1.9 s pit stop — the weekend’s fastest — thanks to upgraded pneumatic jacks with 20 bar boost pressure.
These split-second decisions were guided by live tire-thermal imagery and simulation feeds in each pit wall’s cloud-connected ops center.
Advanced Pit Stop Technology
Modern F1 pit crews are supported by AI-powered vision systems that track wheel-nut alignment and predict glove-to-wheel interactions. Each team deploys high-speed cameras (1,000 fps) and torque sensors on wheel guns, feeding real-time metrics into ML models that adjust pneumatic pressure on the fly. According to a senior Ferrari race engineer, “Our latest pit-stop rig reduced average removal time by 150 ms, a margin that translates to half a grid position over a season.” Unlike NASCAR’s full-time athletes, F1 mechanics split roles between car design, trackside setup, and pit operations, making these gains all the more impressive.
Tire Dynamics and Thermal Management
Pirelli’s compounds faced peak surface temperatures of 75 °C in qualifying, dropping to 68 °C during the race. Thermal imaging revealed hotspots on the inner shoulder of the right-front tire, prompting teams to adjust camber settings from –3.40° to –3.10° midweek. Mercedes’ engineers applied a new silica additive in their pre-race blanket cycles, achieving a 5% faster warm-up curve. Alpine’s bespoke tread-block pattern, tested at Silverstone, showed improved heat dissipation but wore faster under lateral loads.
Aerodynamic and Chassis Setup Analysis
The 2025 regulations emphasize ground-effect floors, yet teams still grapple with porpoising. McLaren’s upgraded T-wing package improved underfloor airflow, reducing vertical oscillations by 8 mm peak-to-peak, as measured by their six on-board accelerometers. Ferrari opted for stiffer dampers to maintain consistent rake, trading a minor drag penalty (ΔCD = +0.005) for steadier downforce generation. Experts suggest that as Barcelona testing looms post-break, these setups will evolve with carbon-fiber floor inserts that modulate flex characteristics.
Expert Opinions
“The Hungarian layout magnifies the importance of pit efficiency and tire strategy. With overtakes at a premium, the team that masters both wins on Sundays,” explains Mercedes’ Technical Director.
“Our AI-driven pit-stop analysis has become as crucial as CFD in aero development,” notes McLaren’s Head of Race Engineering.
Championship Implications and Summer Break Outlook
With McLaren drivers narrowly ahead in the standings, the title fight hinges on reliability and continued incremental gains. Factories will shut for two weeks under the FIA summer break rule, halting updates but allowing engineers to recharge. Expect a flurry of correlation tests between wind tunnel data and in-season sensor logs when operations resume ahead of Spa and Monza.
Key Takeaways: Lightning-fast pit stops driven by AI and high-precision hardware, meticulous tire temperature management, and sophisticated aerodynamic balances decide races where on-track passes are scarce.